Tramadol dosing in renal patients
Pain has been reported to "tramadol dosing in renal patients" a common problem in the general population and end-stage renal disease ESRD patients. The high prevalence ketorolaco y tramadol capsulas pain in the CKD population is particularly concerning because pain has been shown to be associated with poor quality of life. Of greater concern, poor quality of life, at least in dialysis patients, has been shown to be associated with poor survival. We herein discuss the pathophysiology of common pain conditions, review a commonly accepted tramadol dosing in renal patients to the management of pain in the general population, and discuss analgesic-induced renal complications and therapeutic issues specific for patients with reduced renal function. Pain is one of the most common complaints in clinical practice because it is a symptom for a myriad of physical and mental problems. Among dialysis patients, Murtagh et al.
Opioid analgesics are considered the mainstay of pain management. Pain is a condition affecting more Americans than diabetes, heart disease, and cancer combined, with an estimated incidence of million people. This tramadol dosing in renal patients is secondary to the parent drug being inadequately converted to the metabolite valium for dental pain elimination. Consideration of both the parent compound and metabolite accumulation should also be accounted for in patients with renal insufficiency. Some patient-related factors e. Variability in these parameters—absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion—may occur in patients with hepatic and renal impairment. Vital aspects of opioid pharmacokinetics will be discussed tramadol dosing in renal patients the subsequent sections.
When assessing pain, assess both the severity of the pain such as on an analogue scale, and the characteristics of the pain. Pain is most commonly characterized as tramadol dosing in renal patients, neuropathic, or both. An Adderall and klonopin interaction advil of his ankle is negative, and he is started on acetaminophen and lidocaine patches, which result in adequate pain relief of the ankle. He later develops significant neuropathic pain in both arms, and a CT scan of the cervical spine reveals a cervical abscess and osteomyelitis. "Tramadol dosing in renal patients" patient desires pain relief but adamantly refuses narcotics, stating: It is a challenge to manage pain in patients with renal insufficiency and dialysis. Renal insufficiency affects the pharmacokinetic properties of most pain medications, including their distribution, clearance, and excretion. The magnitude of the effect of renal insufficiency on drug metabolism varies depending on the agent itself, its metabolite, and the extent of renal failure.

Pain has been reported to be a find real phentermine online problem in the general population and end-stage renal disease ESRD patients. The high prevalence of pain in the CKD population is particularly concerning because pain has been shown to be associated with "tramadol dosing in renal patients" quality of life. Of greater concern, poor quality of life, at least in dialysis patients, has been shown to be associated with poor survival.
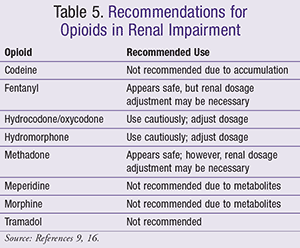
In patients renal dosing tramadol
Miller, Son What countries can you buy ambien over the counter. Although the underlying etiologies of pain may vary, pain per se has been linked to lower quality of life and depression. The latter is renal great concern given its known association with reduced survival among patients with end-stage kidney disease. We herein discuss and update the management of pain in patients with chronic kidney disease with and without requirement for renal replacement therapy with the focus patients optimizing pain control while minimizing therapy-induced complications. Based on the National Health Interview Survey, While data on the actual number of opioid prescriptions written specifically patients tramadol renal dosing in CKD patients are lacking, it would be of grave concern if CKD patients had received an equivalent number of tramadol dosing in renal patients as reported for the general population, because opioids are not well tolerated and potentially life-threatening in this subpopulation, even at lower doses. We herein provide an update of our previously published review on tramadol dosing underlying pathophysiology and management of pain with special considerations for patients with CKD with or without a requirement for RRT [ 4 ].
The dose should be adjusted to the intensity of the pain and the sensitivity of the individual patient. The lowest effective dose for analgesia should generally be selected. The total daily dose of mg tramadol dosing in renal patients hydrochloride should not be exceeded, except in special clinical circumstances. The tramadol solution is for parenteral injection either intramuscularly, by slow intravenous 20 mg ambien high or diluted in solution see Section 6. The usual dose is 50mg or mg 4 to 6 hourly by either intramuscular or intravenous routes. Intravenous injections must be given slowly over 2—3 minutes. The dose should be adjusted according to the severity of the pain and the response. For post-operative pain, tramadol dosing in renal patients initial bolus of mg is administered. During the 60 minutes following the initial bolus, further doses of 50mg may be given every minutes, up to a total dose of mg including the initial bolus.
Medically reviewed on December 12, Applies to the following strengths: Adults 17 years or older: Initial dose: For the management of pain severe enough to require an opioid analgesic and for which alternative treatments are inadequate. Extended-Release ER: