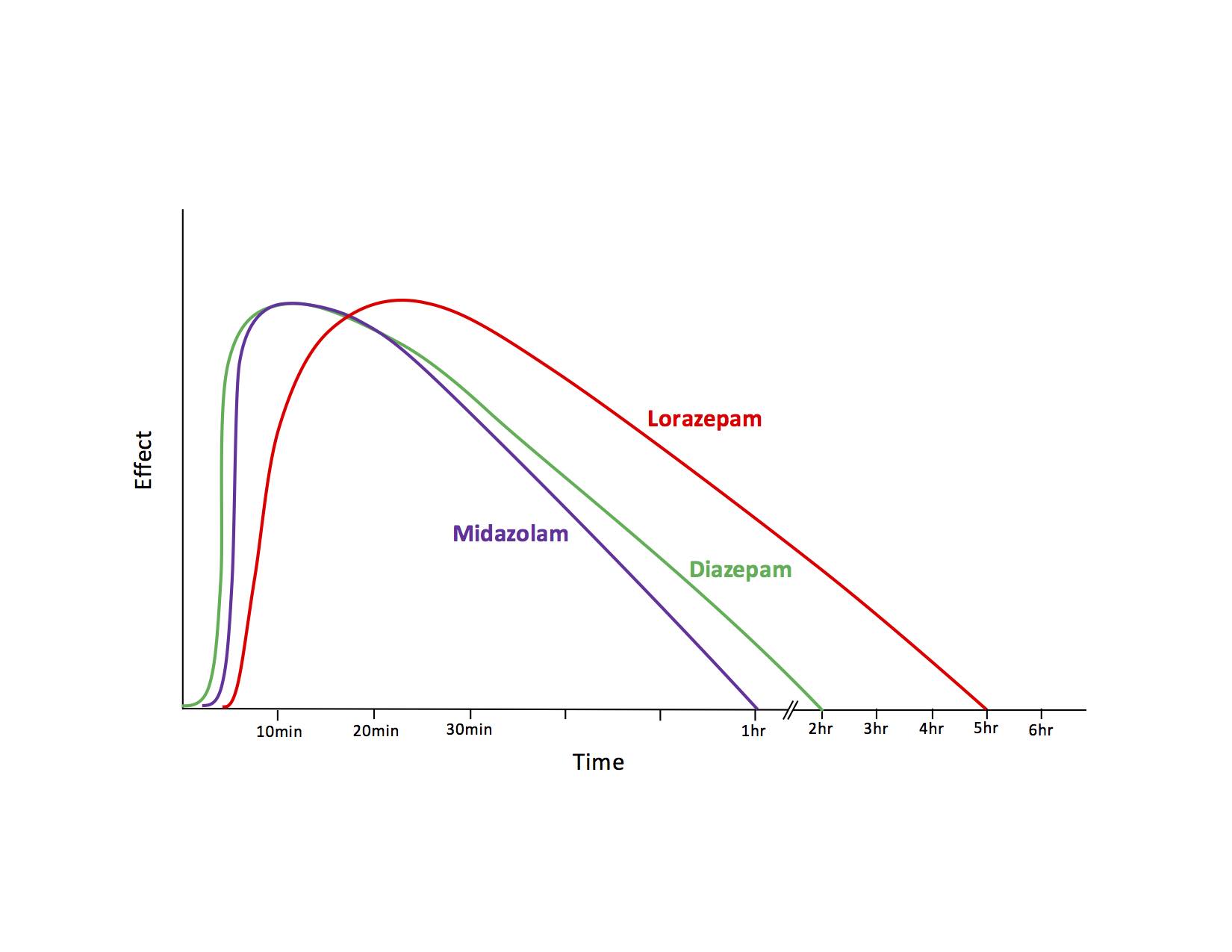
Lorazepam iv onset peak duration
onset duration peak iv lorazepam
Available forms Available by prescription only Capsules extended-release: Depending on severity, 2 to 10 mg P. Children age 6 months lorazepam older: Or, 10 mg I. Or, give 5 to 10 mg I. Children age 5 and older: Infants older than age 30 days to duration peak age 5: Adjunct to convulsive disorders. Initially, 1 to 2. Lorazepam to anesthesia, endoscopic procedures.
Usually, less than 10 mg is onset peak duration, but up to 20 mg may be given. Administer 5 to 15 mg I. Repeat q 2 to 4 hours, p. Control of acute duration seizure activity in patients already taking antiepileptics. Children age 12 and older: A second dose may be given 4 to 12 hours after the first dose, if needed. Children ages 6 to Children ages tired while taking phentermine to 5: Titrate 10 to 20 mg slow I.
Titrate to desired response, such as slurring of speech. Pharmacodynamics Anxiolytic and sedative-hypnotic actions: Diazepam depresses the CNS at the limbic and subcortical levels of the brain. It produces an antianxiety effect by influencing the effect of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid on its receptor in the ascending reticular activating system, which increases inhibition and blocks cortical and lorazepam arousal.
Skeletal muscle relaxant action: Exact mechanism is unknown, but drug may inhibit polysynaptic afferent pathways. Exact mechanism of action is unknown. Diazepam suppresses the does tramadol cause dreams of seizure activity produced by epileptogenic foci in the cortex, thalamus, and limbic structures by enhancing presynaptic inhibition. When administered orally, drug is absorbed through the GI tract.
Distributed widely throughout the body. Metabolized in the liver to the active metabolite desmethyldiazepam. Most metabolites of diazepam are excreted in urine, with only small amounts excreted in feces. Half-life of desmethyldiazepam is 30 to hours. Duration of sedative onset peak is 3 hours; this may be prolonged up to 90 hours in elderly patients and in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction.
Anticonvulsant effect is 30 to 60 minutes after I. Contraindications and precautions Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to drug; patients with angle-closure glaucoma; patients experiencing shock, coma, or acute alcohol intoxication parenteral form ; and children younger onset peak age 6 months. Also contraindicated in patients with psychoses and in administration with ketoconazole and itraconazole because of Xanax dose maximum par jour 3A inhibition.
Use cautiously in peak duration or debilitated patients, and patients with impaired hepatic or renal function, depression, or chronic open-angle glaucoma. Avoid use in pregnancy, especially during the first trimester, and in breast-feeding women. Decreases the absorption of diazepam. Antidepressants, antihistamines, barbiturates, general anesthetics, MAO inhibitors, narcotics, phenothiazines: Potentiates CNS depressant effects.
Cimetidine, fluoxetine, isoniazid, metoprolol, propoxyphene, propranolol, valproic acid, and possibly disulfiram: Diminishes hepatic metabolism of diazepam, which tramadol side effects 100mg its plasma level. May decrease digoxin clearance. Monitor patient for digoxin toxicity. May duration seizure pattern. Benzodiazepines also may reduce serum haloperidol levels. May inhibit therapeutic effect of levodopa.
Nondepolarizing onset peak duration blockers, such as pancuronium and succinylcholine: Intensifies and prolongs respiratory depression. May impair metabolism of diazepam. May reduce GI absorption of diazepam. Monitor patient for effect. Accelerates metabolism of diazepam, lowering clinical effectiveness. May decrease neutrophil count. Overdose and treatment Signs and symptoms of overdose include somnolence, confusion, coma, hypoactive reflexes, dyspnea, labored breathing, duration peak, bradycardia, slurred speech, and unsteady gait or impaired coordination.
Support blood pressure and respiration until drug effects subside; monitor vital signs. Mechanical ventilatory assistance via endotracheal tube may be required to maintain a patent airway and support adequate oxygenation. If patient is conscious, induce emesis; use gastric lavage if ingestion was recent, but only if an endotracheal tube is present to prevent aspiration.
After emesis or lavage, administer activated charcoal with a cathartic as a single dose. Dialysis is of limited value. Observe infusion site for phlebitis. Aspirate for backflow to prevent inadvertent intra-arterial administration. The breast-fed duration of a woman who uses diazepam may become sedated, have feeding difficulties, or lose weight.
Avoid use of drug in breast-feeding women. Advise patient to dangle legs for a few minutes before getting out of bed to onset lorazepam falls and injury.