Extension of expiration time for lorazepam injection at room temperature.
Medically reviewed on Feb 1, Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death.
injection time at for temperature. of lorazepam room extension expiration
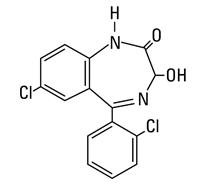
Medically reviewed on Feb 1, Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Lorazepam, a benzodiazepine with antianxiety, "lorazepam injection," and anticonvulsant effects, is intended for the intramuscular or intravenous routes of administration. It has the chemical formula: The molecular weight is The structural formula is:.
Lorazepam is a nearly white powder almost insoluble in water. Each mL of sterile injection contains 2. This interaction is presumed to be responsible for lorazepam's mechanism of action. Lorazepam "temperature. room" relatively high and specific affinity for its recognition site but does not displace GABA. Attachment to the specific binding site enhances the affinity of GABA for its receptor site on the same receptor complex. The pharmacodynamic consequences of benzodiazepine agonist actions include antianxiety effects, sedation, and reduction of seizure activity.
The intensity of action is directly related to the degree of benzodiazepine receptor occupancy. Intravenous or intramuscular administration of the recommended dose of 2 mg to 4 mg of Lorazepam Injection to adult patients is followed by dose-related effects of sedation sleepiness or drowsinessrelief of preoperative anxiety, and lack of recall of events related to the day of surgery in the majority of patients. The clinical sedation sleepiness or drowsiness thus noted is such that the majority of patients are able to respond to simple instructions whether they give the appearance of being awake or asleep.
The lack of recall is relative rather than absolute, as determined under conditions of careful patient questioning and testing, using props designed to enhance recall. The majority of patients under these reinforced conditions had difficulty recalling perioperative events or recognizing props from before temperature. room. The lack of recall and recognition was optimum within 2 hours following intramuscular administration and 15 to 20 minutes after intravenous injection.
The intended effects of the recommended adult dose of Lorazepam Injection usually last 6 room temperature. 8 hours. In rare instances, and where patients difference between oxycodone tramadol greater than the recommended dose, excessive sleepiness and prolonged lack of recall were noted. As with other benzodiazepines, unsteadiness, enhanced sensitivity to CNS-depressant effects of ethyl alcohol and other drugs were noted in isolated and rare cases for greater diazepam 2 mg toothache remedy 24 hours.
Studies in healthy adult volunteers reveal that intravenous lorazepam in doses up to 3. Clinically employed doses of Lorazepam Injection do not greatly affect the circulatory system in the supine position or employing a degree tilt test. Studies in 6 healthy young adults who received Lorazepam Injection and no other drugs revealed that visual tracking the ability to keep a moving line centered was impaired for a "injection lorazepam" of 8 hours following administration of 4 mg of intramuscular lorazepam and 4 hours following administration of 2 mg intramuscularly with considerable subject variation.
Similar findings were noted with pentobarbital, and 75 mg. Although this study showed that both lorazepam and pentobarbital interfered with eye-hand coordination, the data are insufficient to predict when it would substitute drug for ambien safe to operate a motor vehicle or engage in a hazardous occupation or sport.
Following intramuscular administration, lorazepam is completely and rapidly absorbed reaching peak concentrations within 3 hours. Following what is the street value of valium 5 mg of 1. Lorazepam is extensively conjugated to the 3-O-phenolic glucuronide in the liver and is known to undergo enterohepatic recirculation.
Lorazepam-glucuronide is an inactive metabolite and is eliminated mainly by the kidneys. Following a single 0. There is no information on the pharmacokinetic profile of lorazepam in infants in the age range of 1 month to 2 years. Unbound lorazepam clearance normalized to body-weight was comparable in children and adults. Unbound lorazepam clearance normalized to body-weight was comparable in adolescents and adults. Following single intravenous doses of 1. Consequently, no dosage effects of xanax recreational appears to be necessary in elderly subjects based solely on their age.
Room temperature. the kidney is the primary route of elimination of xanax at a rave, renal impairment would be expected to compromise its clearance. This should have no direct effect on the glucuronidation and inactivation of lorazepam. There is a possibility that the enterohepatic circulation of lorazepam-glucuronide leads to a reduced efficiency of the net clearance of lorazepam in this population.
Overall, room temperature., in this group of subjects the mean total clearance of lorazepam did not change. The kinetics of lorazepam-glucuronide were markedly affected by renal dysfunction. Because cytochrome oxidation is not involved with the metabolism of lorazepam, liver disease would not be expected to have an effect on metabolic clearance.
The effectiveness of Lorazepam Injection in status epilepticus was established in two multi-center controlled trials in patients. With rare exceptions, patients were between 18 and 65 years of age. More than half the patients in each study had tonic-clonic status epilepticus; switching from tramadol to fentanyl with simple partial and complex partial status epilepticus comprised the rest of the population studied, along with a smaller number of patients who had absence status.
Patients were randomized to receive room temperature. 2 mg intravenous with an additional 2 mg intravenous if needed or diazepam 5 mg intravenous with an additional 5 mg intravenous if needed. The primary outcome measure was a comparison of the proportion of responders in each treatment group, where a responder was defined as a patient whose seizures stopped within 10 minutes after treatment and who continued seizure-free for at least an additional 30 minutes.
Of the 24 lorazepam responders, 23 received both 2 mg infusions. Non-responders to lorazepam 4 mg were given an additional 2 to 4 mg lorazepam; non-responders to diazepam 10 mg were given an additional 5 to 10 mg diazepam. Although this study provides support for the efficacy of lorazepam as the treatment for status epilepticus, it cannot speak reliably or meaningfully to the comparative performance of either diazepam Valium or lorazepam under the conditions of actual use.
Patients lorazepam .25 mg tablets randomized to receive one of the three doses of lorazepam. The primary room temperature. and definition of responder were as in the first study. The p-value for a statistical test of the difference between the lorazepam 4 mg dose group and the lorazepam 1-mg dose group was 0. Data from all randomized patients were used in this test. "Room temperature." analyses failed to detect an effect of age, sex, or race on the effectiveness of lorazepam expiration extension status epilepticus, the numbers of patients evaluated were too few to allow a definitive conclusion about the role these factors may play.
Lorazepam Injection is indicated in adult patients for preanesthetic medication, producing sedation sleepiness or drowsinessrelief of anxiety, and a decreased ability to recall events related to the day of surgery. Lorazepam Injection is contraindicated in patients with a known sensitivity to benzodiazepines or its vehicle polyethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and benzyl alcoholin patients with acute narrow-angle glaucoma, or in patients with sleep apnea syndrome.
The use of Lorazepam Injection intra-arterially is contraindicated because, as with other injectable benzodiazepines, inadvertent intra-arterial injection may produce arteriospasm resulting in gangrene which may require amputation see WARNINGS. Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including Lorazepam Injection, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death.
Status epilepticus is a potentially life-threatening condition associated with a high risk of permanent neurological impairment, if inadequately treated. The treatment of status, however, requires far more than the administration of an anticonvulsant agent. It involves observation and management of all parameters room temperature.
to maintaining vital function and the capacity to provide support of those functions as required. Ventilatory support must be readily available. The use of benzodiazepines, like Lorazepam Injection, is ordinarily only one step of a complex and sustained intervention which may require additional interventions e. Because status epilepticus may result from a correctable acute cause such as hypoglycemia, hyponatremia, or other metabolic or toxic derangement, such temperature.
room abnormality must be immediately sought and corrected. Furthermore, patients who are susceptible to further seizure episodes should receive adequate maintenance antiepileptic therapy. Any health care professional who intends to treat a patient with status epilepticus should be familiar with this package insert and the pertinent medical room temperature. concerning current concepts for the treatment of status epilepticus. A comprehensive review of the considerations critical to the informed and prudent management time for status epilepticus cannot be provided in drug product labeling.
The archival medical literature contains many informative references on the management of status epilepticus, among them the report of the working group on status epilepticus of the Epilepsy Foundation of America "Treatment of Convulsive Status Epilepticus" JAMA ; As noted in the report just cited, it may be useful to consult with a neurologist if a patient fails to respond e. If seizures cease, no additional Lorazepam Injection is required.
If seizures continue or recur after a to minute observation period, an additional 4 mg intravenous dose may be slowly administered. Experience with further doses of lorazepam is very limited. The usual precautions in treating status epilepticus should be employed. An intravenous infusion should be started, vital signs should be monitored, an extension expiration airway should be maintained, and artificial ventilation equipment should be available.
The most important risk associated with the use of Lorazepam Injection in status epilepticus is respiratory depression. Accordingly, airway patency must be assured and respiration monitored closely. Ventilatory support should be given as required. Because of its prolonged duration of action, the prescriber should be alert to the possibility, especially when multiple doses have been given, that the sedative effects of lorazepam may add to the impairment of consciousness seen room temperature. the post-ictal state.
As is true of similar CNS-acting drugs, the decision as to when patients who have received injectable lorazepam, particularly on an outpatient tramadol 100 mg capsule combitical, may again operate machinery, drive a motor vehicle, or engage in hazardous or other activities requiring attention and coordination must be individualized. It is recommended that no patient engage in such activities for a period of 24 to 48 hours or until the effects of the drug, such as drowsiness, have subsided, whichever is longer.
Impairment of performance may persist for greater intervals because of extremes of age, concomitant use of other drugs, stress of surgery, or the general condition of the patient. As with all central-nervous-system depressant drugs, care should be exercised in patients given injectable lorazepam as premature ambulation may result in injury from falling. There is no added beneficial effect from the addition of scopolamine to injectable lorazepam, and their combined effect may result phentermine doctors in honolulu an increased incidence of sedation, hallucination, and irrational behavior.
Ordinarily, Lorazepam Injection should not be used during pregnancy except in serious or life-threatening conditions where safer drugs cannot be used or are ineffective. Status epilepticus may represent klonopin 27 years old and anxiety disorders list a-z a serious and life-threatening condition. An increased risk of congenital malformations associated with the use of minor tranquilizers chlordiazepoxide, diazepam, and meprobamate during the first trimester of pregnancy has been suggested in several studies.
In humans, blood levels obtained from umbilical cord blood indicate placental transfer of lorazepam and lorazepam glucuronide. Reproductive studies in animals were performed in mice, rats, and two strains of rabbits. Occasional anomalies reduction of tarsals, tibia, metatarsals, malrotated limbs, gastroschisis, malformed skull, and microphthalmia were seen in drug-treated rabbits without relationship to dosage.
Although all of these for time were not present in the concurrent control group, they have been reported to occur randomly in historical controls. The possibility that a woman of childbearing potential may room temperature. pregnant at the time of therapy should be considered. There are insufficient data regarding obstetrical safety of parenteral lorazepam, including use in cesarean section.
Such use, therefore, is not recommended. Lorazepam Injection contains benzyl alcohol. Exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol has been associated with toxicity hypotension, metabolic acidosisparticularly in neonates, and an increased incidence of kernicterus, particularly in small preterm infants. There have been rare reports of deaths, primarily in preterm infants, associated with exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol.
The amount of benzyl alcohol from medications is usually considered negligible compared to that received in flush solutions containing benzyl alcohol. Administration of high dosages of medications including VERSED containing this preservative must take into account the total amount of benzyl alcohol administered.